The ability to store data in files is a core element of any computing system.most organizations, important data files are stored centrally in some kind of shared file storage system. Increasingly, that central storage location is hosted in the cloud, enabling cost-effective, secure, and reliable storage for large volumes of data.
The specific file format used to store data depends on a number of factors, including:
- The type of data being stored (structured, semi-structured, or unstructured).
- The applications and services that will need to read, write, and process the data.
- The need for the data files to be readable by humans, or optimized for efficient storage and processing.
Delimited text files
Data is often stored in plain text format with specific field delimiters and row terminators. The most common format for delimited data is comma-separated values (CSV) in which fields are separated by commas, and rows are terminated by a carriage return / new line. Optionally, the first line may include the field names. Other common formats include tab-separated values (TSV) and space-delimited (in which tabs or spaces are used to separate fields), and fixed-width data in which each field is allocated a fixed number of characters. Delimited text is a good choice for structured data that needs to be accessed by a wide range of applications and services in a human-readable format.
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)
JSON is a ubiquitous format in which a hierarchical document schema is used to define data entities (objects) that have multiple attributes. Each attribute might be an object (or a collection of objects); making JSON a flexible format that's good for both structured and semi-structured data.
The following example shows a JSON document containing a collection of customers. Each customer has three attributes (firstName, lastName, and contact), and the contact attribute contains a collection of objects that represent one or more contact methods (email or phone). Note that objects are enclosed in braces ({..}) and collections are enclosed in square brackets ([..]). Attributes are represented by name : value pairs and separated by commas (,).
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
XML is a human-readable data format that was popular in the 1990s and 2000s. It's largely been superseded by the less verbose JSON format, but there are still some systems that use XML to represent data. XML uses tags enclosed in angle-brackets (<../>) to define elements and attributes, as shown in this example:
Binary Large Object (BLOB)
Ultimately, all files are stored as binary data (1's and 0's), but in the human-readable formats discussed above, the bytes of binary data are mapped to printable characters (typically through a character encoding scheme such as ASCII or Unicode). Some file formats however, particularly for unstructured data, store the data as raw binary that must be interpreted by applications and rendered. Common types of data stored as binary include images, video, audio, and application-specific documents.
When working with data like this, data professionals often refer to the data files as BLOBs (Binary Large Objects)
Optimized file formats
While human-readable formats for structured and semi-structured data can be useful, they're typically not optimized for storage space or processing
Some common optimized file formats you might see include Avro, ORC, and Parquet:
Avro is a row-based format. It was created by Apache. Each record contains a header that describes the structure of the data in the record. This header is stored as JSON. The data is stored as binary information. An application uses the information in the header to parse the binary data and extract the fields it contains. Avro is a good format for compressing data and minimizing storage and network bandwidth requirements.
Below is a basic sample file of Avro schema.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | { "type": "record", "name": "thecodebuzz_schema", "namespace": "thecodebuzz.avro", "fields": [ { "name": "username", "type": "string", "doc": "Name of the user account on Thecodebuzz.com" }, { "name": "email", "type": "string", "doc": "The email of the user logging message on the blog" }, { "name": "timestamp", "type": "long", "doc": "time in seconds" } ], "doc:": "A basic schema for storing thecodebuzz blogs messages"} |
ORC (Optimized Row Columnar format) organizes data into columns rather than rows. It was developed by HortonWorks for optimizing read and write operations in Apache Hive (Hive is a data warehouse system that supports fast data summarization and querying over large datasets). An ORC file contains stripes of data. Each stripe holds the data for a column or set of columns. A stripe contains an index into the rows in the stripe, the data for each row, and a footer that holds statistical information (count, sum, max, min, and so on) for each column.
Parquet is another columnar data format. It was created by Cloudera and Twitter. A Parquet file contains row groups. Data for each column is stored together in the same row group. Each row group contains one or more chunks of data. A Parquet file includes metadata that describes the set of rows found in each chunk. An application can use this metadata to quickly locate the correct chunk for a given set of rows, and retrieve the data in the specified columns for these rows. Parquet specializes in storing and processing nested data types efficiently. It supports very efficient compression and encoding schemes.
databases
Relational databases
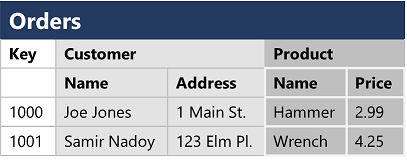
Relational databases are commonly used to store and query structured data. The data is stored in tables that represent entities, such as customers, products, or sales orders. Each instance of an entity is assigned a primary key that uniquely identifies it; and these keys are used to reference the entity instance in other tables.
Non-relational databases
Non-relational databases are data management systems that don’t apply a relational schema to the data. Non-relational databases are often referred to as NoSQL database, even though some support a variant of the SQL language.
There are four common types of Non-relational database commonly in use.
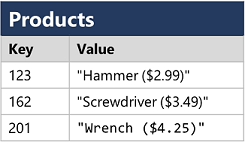
Key-value databases in which each record consists of a unique key and an associated value, which can be in any format.
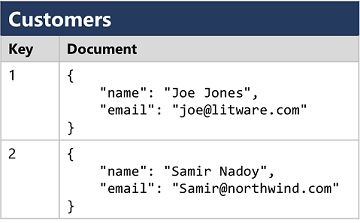
Document databases, which are a specific form of key-value database in which the value is a JSON document (which the system is optimized to parse and query)
Column family databases, which store tabular data comprising rows and columns, but you can divide the columns into groups known as column-families. Each column family holds a set of columns that are logically related together.
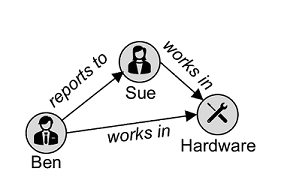
Graph databases, which store entities as nodes with links to define relationships between them.